While India’s Chandrayaan-2 mission didn’t go exactly to plan, there is still a lot to gain from the mission.
This article could be used with students studying Physical or Earth and Space Sciences in year 7 and 10. It would provide a good opportunity to discuss Australia’s future in space exploration as well as the positives of failure.
Word Count: 772
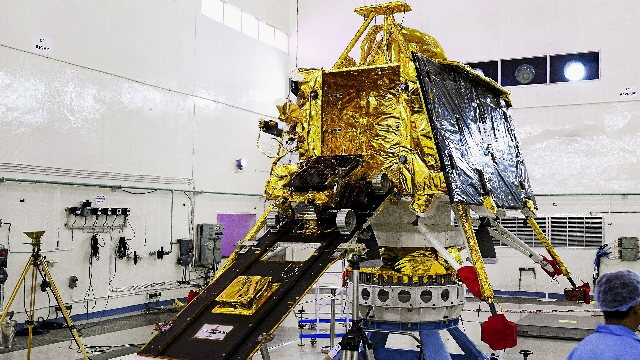
Over the weekend, India attempted to make history by becoming just the fourth nation to successfully land a probe on the Moon. It came agonisingly close, but after journeying millions of kilometres, the Vikram lander lost contact in the final few hundred metres and crash-landed on the lunar surface.
But it would be both unfair and plain wrong to label the mission a failure.
The two-month trip
After a postponed launch, India’s Chandrayaan-2 spacecraft began its journey to the Moon on July 22.
Onboard it carried the Vikram lander and Pragyan rover, equipped to search the lunar south pole for water and other valuable resources. Everything seemed to be going according to plan. Chandrayaan-2 completed several orbits around Earth and then the Moon, slowly making its way closer to the lunar surface and taking photographs the whole time.
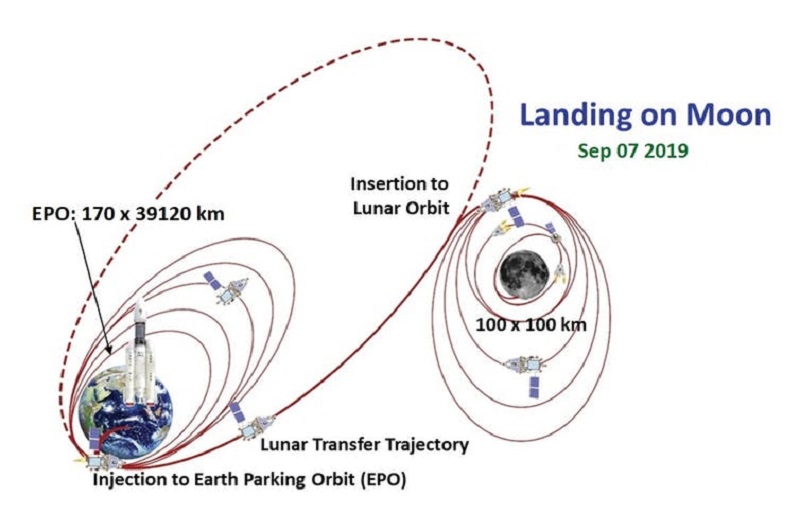
On September 2, the Vikram lander separated and began to make its descent. All communications were normal until the lander was within 2km of its goal.
Then it went silent – a space engineer’s worst nightmare.
Vikram, do you copy?
So far, the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) engineers have not been able to reestablish communications with the lander. It’s likely Vikram landed with enough force to damage its communications equipment, as well as other instruments.
But all hope was not lost, as Chandrayaan-2 remained in orbit above the Moon and, with its high-resolution camera, was able to spot the lander. If oriented favourably, Vikram could still manage to power itself up.
ISRO has not admitted defeat and will keep trying to connect to Vikram for the next two weeks. However, the chances of success diminish with time.
While the Chandrayaan-2 mission has not gone as expected, it cannot be called a failure. The Chandrayaan-2 orbiter will continue to monitor the Moon for up to seven years and the high-resolution images it takes will be vital to future international efforts to land on the Moon.
India’s moon mission is technically a success
The near success of Vikram’s landing should be celebrated. To appreciate just how hard it is, let’s delve into some physics.
Earth is rotating and also hurtling through space at more than 100,000km per hour. The Moon is almost 400,000km away and travelling around 4,000km per hour as it orbits Earth.

To reach the Moon, you first have to escape Earth’s gravity and ensure you’re going at the right speed to orbit Earth a few times before moving far enough to be caught by the Moon. Then you slowly decrease your distance to the lunar surface, inching closer over several orbits until you are low enough to use powered assistance to land.
It took the United States and Russia decades to design, plan and execute missions to the Moon. In fact, the ISRO was founded shortly after the successful Apollo 11 mission.
We should applaud the hard work India has done over the past 50 years to get this far. This sentiment was clear as Indian prime minister Narendra Modi addressed his country, all of whom stood in solidarity with the scientists who spent countless hours in pursuit of their goal.
A global space community
The story of the Indian lander echoes that of the failed Israeli landing attempt earlier this year.
The Beresheet lander was built by private company SpaceIL, which was chasing the coveted Google Lunar XPrize when an engine malfunction caused it to swan dive into the Moon’s surface.
I mention this mission to reiterate just how hard the task is, but also to demonstrate that the old Cold War space superpowers are no longer the only ones in the game. Countries and even private companies across the world are gaining spacefaring capabilities and undertaking incredible missions that will enable humankind to go further than ever before.
But as the cliché goes, with great power comes great responsibility.
Now that countries across the world can send things into space, we must have solidarity as a global spacefaring community to consider how our actions up there will affect us on Earth and to ensure long-term success in space ventures.
This is not the last international space mission you will hear about in the news this year.
In coming years, we may even be discussing Australian ventures into space – and maybe even to the Moon itself.
![]()
Rebecca Allen, Swinburne Space Office Project Coordinator | Manager Swinburne Astronomy Productions, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Login or Sign up for FREE to download a copy of the full teacher resource